Title: Understanding Hedge Funds: Strategies, Risks, and Considerations
Understanding Hedge Funds: Strategies, Risks, and Considerations
Hedge funds are complex investment vehicles that employ various strategies to generate returns for their investors. Unlike traditional investment funds, hedge funds typically have more flexibility in their investment approach and can use leverage, derivatives, and other sophisticated techniques to achieve their objectives.
Hedge funds are characterized by several key features:
- Alternative Investments: Hedge funds often invest in alternative asset classes such as derivatives, currencies, commodities, and real estate, in addition to stocks and bonds.
- Performance Incentives: Hedge fund managers typically receive both a management fee (usually a percentage of assets under management) and a performance fee (a percentage of profits).
- Flexibility: Hedge funds have more flexibility than traditional investment funds in terms of investment strategies, asset allocation, and risk management techniques.
- Limited Regulation: Compared to mutual funds, hedge funds are subject to less regulatory oversight, allowing managers to pursue a wider range of investment opportunities.
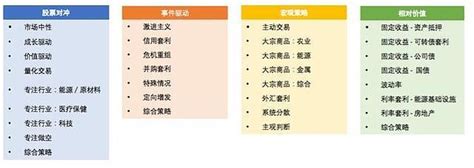
There are numerous hedge fund strategies, each with its own riskreturn profile. Some common strategies include:
- Long/Short Equity: Hedge funds take long positions in stocks they believe will increase in value and short positions in stocks they expect to decline.
- Global Macro: Managers take positions in various asset classes based on their views on macroeconomic trends and geopolitical events.
- EventDriven: Hedge funds invest in securities of companies involved in corporate events such as mergers, acquisitions, bankruptcies, and restructurings.
- Quantitative: Managers use mathematical models and algorithms to identify trading opportunities based on statistical analysis.
- Distressed Debt: Funds invest in the debt of companies that are experiencing financial distress or bankruptcy, with the aim of profiting from the eventual recovery of the debt.
While hedge funds offer the potential for high returns, they also come with significant risks and considerations:
- High Fees: Hedge funds typically charge higher fees compared to traditional investment funds, which can eat into investors' returns, especially during periods of underperformance.
- Complexity: Hedge fund strategies can be highly complex and difficult to understand, making it challenging for investors to assess their risk exposures and performance drivers.
- Lack of Liquidity: Many hedge fund investments have lockup periods during which investors cannot redeem their shares, limiting liquidity and potentially causing difficulties during market downturns.
- Counterparty Risk: Hedge funds often use derivatives and other financial instruments, exposing them to counterparty risk if the counterparties fail to meet their obligations.
- Regulatory Risks: Changes in regulatory requirements or market conditions can impact hedge fund operations and performance, potentially leading to losses for investors.
For investors considering hedge funds as part of their portfolio, it's essential to:
- Conduct Due Diligence: Thoroughly research and understand the investment strategy, track record, and risk management practices of the hedge fund manager.
- Assess Fit: Evaluate whether hedge funds align with your investment objectives, risk tolerance, and overall portfolio strategy.
- Diversify: Avoid overconcentration in hedge funds and maintain a diversified portfolio across asset classes and investment strategies.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly review the performance of hedge fund investments and reassess their role in your portfolio over time.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consider consulting with financial advisors or consultants experienced in alternative investments to help navigate the complexities of hedge fund investing.